In today’s fast-paced business landscape, the ability to seamlessly integrate and manage data from various sources is crucial for profitability and performance. SAP Profitability and Performance Management (PaPM) provides a powerful solution to address these challenges by offering robust data flow and integration capabilities across SAP and non-SAP systems.
In this blog post, we will explore the key aspects of data flow and integration within PaPM, focusing on how data is accessed, processed, and written between systems. We’ll also discuss the traceability of data, why it matters for decision-making, and the tools and interfaces that SAP PaPM offers to handle diverse data sources. Finally, we will share examples of how these integrations work in real-world scenarios and offer insights into best practices for optimizing PaPM in your business environment.
Data Flow and Integration
SAP Profitability and Performance Management is a solution that enables you to improve your business processes by collecting data from SAP and non-SAP systems.
SAP Profitability and Performance Management can be deployed in both cloud and on-premises environments and provide a variety of integration options. This integration can operate between SAP and non-SAP systems.
The traceability of the data is the most important thing for a key user who analyses the results and is responsible for reporting to higher levels. Data can be enriched with calculations, derivations, and unifying other datasets while data is flowing between the data sources. For optimal results, it’s advised by SAP to deploy SAP Profitability and Performance Management as close as possible to the source data.
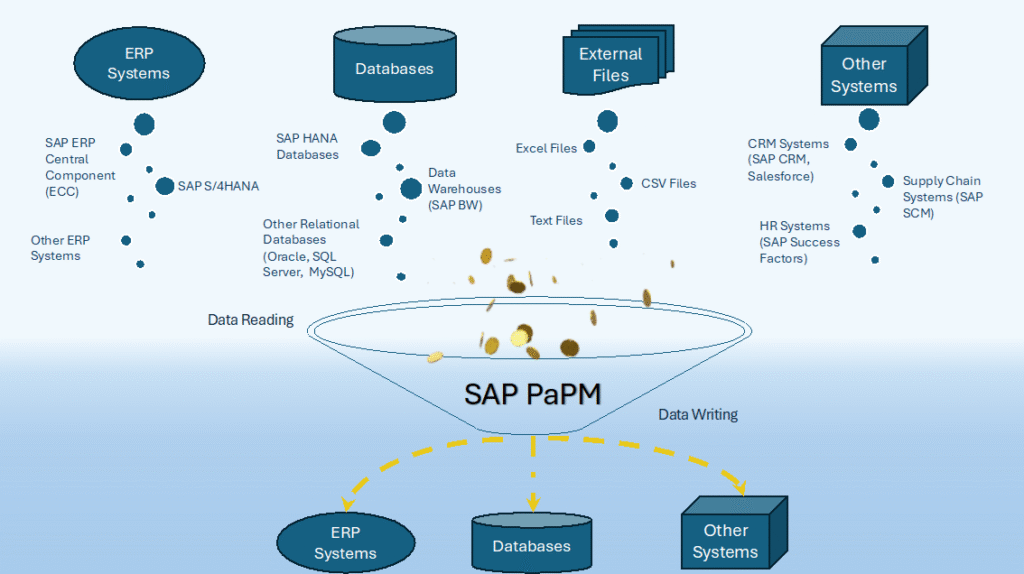
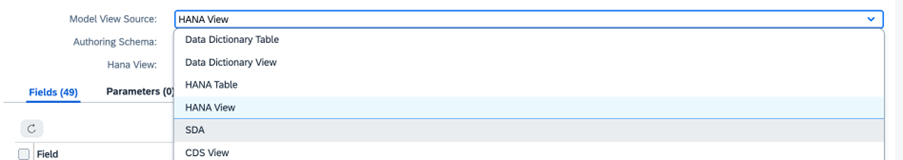
SAP Profitability and Performance Management supports data read access through standard interfaces from SAP or non-SAP applications. For example, it can leverage CDS views from SAP HANA or SAP S/4HANA, open ODS views from SAP BW or BW/4HANA, and calculation views from sources like CAR, FSDM, or BDMA. These can be accessed either locally or through smart data access remotely. Should redundancy-free access not be possible, alternative options like SAP BAPIs, web services, or file imports in different formats are used.
When writing data, SAP Profitability and Performance Management also uses official SAP or non-SAP interfaces. This includes options such as HAP to BW or BW/4HANA, SAP HANA-based PAK functions for BPC, and AMDP interfaces to the Results Data component. If redundancy-free operations aren’t feasible, alternative methods, like SAP BAPIs or file exports in various formats, are available.
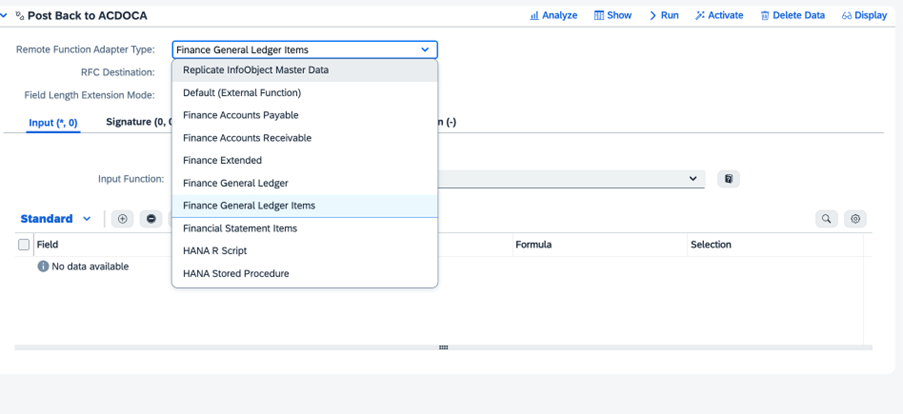
For example, you can access input data source such as S4HANA using Smart Data Access (SDA), modify input data based on business requirements in PaPM, then you can send the results to outsource system S4HANA with using SAP BAPIs. The appropriate data access and write options can be decided based on business requirements and system diversity.





